Problem Statement
The challenge of arranging n queens on a n × n chessboard so that no two queens attack one another is known as the "n-queens puzzle".
Return every unique solution to the n-queens puzzle given an integer n. The answer can be returned in any sequence.
Every solution has a unique board arrangement for the placement of the n-queens, where 'Q' and '.' stand for a queen and an empty space, respectively.
Examples
Example 1:
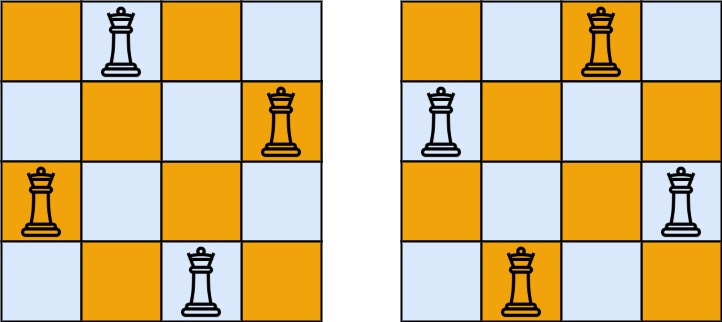
Input: n = 4
Output: [
[". Q . .", ". . . Q", "Q . . .", ". . Q ."],
[". . Q .", "Q . . .", ". . . Q", ". Q . ."]
]
Explanation:
There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle.Example 2:
Input: n = 2
Output: [[]]
Explanation: There is no possible combination for placing two queens on a board of size 2*2.Example 3:
Input: n = 1
Output: [["Q"]]Constraints:
1 ≤ n ≤ 9- We can infer that recursion is a suitable approach to solve the problem by looking at the constraints.
Different Approaches
1️⃣ Recursion (Backtracking)
The N-Queens problem is solved using backtracking. We place queens row-by-row, and for each row, we try all columns. A position is valid if no other queen threatens the current cell (column, upper-left diagonal, or upper-right diagonal).
🧠 Core Idea
- Start from the 0th row.
- For each column in the current row, check if it's safe to place a queen.
- If it is:
- Place the queen.
- Recurse to the next row.
- Backtrack (remove the queen).
- If we successfully reach the nth row, we've placed all queens safely → save the board.
Code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
// Check if it's safe to place a queen at board[row][col]
bool safe(vector<string>& board, int row, int col) {
int r = row, c = col;
// Check upper left diagonal
while (r >= 0 && c >= 0) {
if (board[r][c] == 'Q') return false;
r--;
c--;
}
// Reset to the original position
r = row;
c = col;
// Check left side
while (c >= 0) {
if (board[r][c] == 'Q') return false;
c--;
}
// Reset to the original position
r = row;
c = col;
// Check lower left diagonal
while (r < board.size() && c >= 0) {
if (board[r][c] == 'Q') return false;
r++;
c--;
}
// If no queens are found, it's safe
return true;
}
// Function to place queens on the board
void func(int col, vector<vector<string>>& ans, vector<string>& board) {
// If all columns are filled, add the solution to the answer
if (col == board.size()) {
ans.push_back(board);
return;
}
// Try placing a queen in each row for the current column
for (int row = 0; row < board.size(); row++) {
// Check if it's safe to place a queen
if (safe(board, row, col)) {
// Place the queen
board[row][col] = 'Q';
// Recursively place queens in the next columns
func(col + 1, ans, board);
// Remove the queen and backtrack
board[row][col] = '.';
}
}
}
// Solve the N-Queens problem
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
// List to store the solutions
vector<vector<string>> ans;
// Initialize the board with empty cells
vector<string> board(n, string(n, '.'));
// Start placing queens from the first column
func(0, ans, board);
return ans;
}
};
// Main method to test the solution
int main() {
Solution solution;
int n = 4; // Example with 4 queens
vector<vector<string>> solutions = solution.solveNQueens(n);
// Print all solutions
for (const auto& sol : solutions) {
for (const auto& row : sol) {
cout << row << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}class Solution {
public:
// Check if column has any queen upwards
bool isColumnSafe(vector<string>& board, int row, int col, int n) {
while (row >= 0) {
if (board[row][col] == 'Q') return false;
row--;
}
return true;
}
// Check if top-right diagonal is safe
bool isTopRightDiagonalSafe(vector<string>& board, int row, int col, int n) {
while (row >= 0 && col < n) {
if (board[row][col] == 'Q') return false;
row--;
col++;
}
return true;
}
// Check if top-left diagonal is safe
bool isTopLeftDiagonalSafe(vector<string>& board, int row, int col, int n) {
while (row >= 0 && col >= 0) {
if (board[row][col] == 'Q') return false;
row--;
col--;
}
return true;
}
// Validate if it's safe to place a queen at (row, col)
bool isSafe(vector<string>& board, int row, int col, int n) {
return isColumnSafe(board, row, col, n) &&
isTopRightDiagonalSafe(board, row, col, n) &&
isTopLeftDiagonalSafe(board, row, col, n);
}
// Recursive backtracking function
void backtrack(vector<vector<string>>& allSolutions, vector<string>& board, int row, int n) {
// Base Case: All queens are placed
if (row == n) {
allSolutions.push_back(board);
return;
}
// Try placing a queen in each column of this row
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (isSafe(board, row, col, n)) {
board[row][col] = 'Q'; // Place queen
backtrack(allSolutions, board, row + 1, n); // Move to next row
board[row][col] = '.'; // Backtrack: remove queen
}
}
}
// Main function
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
vector<vector<string>> allSolutions;
vector<string> board(n, string(n, '.')); // n x n board initialized with '.'
backtrack(allSolutions, board, 0, n);
return allSolutions;
}
};
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity:
O(n! * n)- For each row, we try up to
ncolumns →O(n!)possibilities (one queen per row and column). - For each placement, we do
O(n)work to validate (upward and 2 diagonals)
- For each row, we try up to
- Space Complexity:
O(n^2)- Board:
O(n^2) - Recursion stack:
O(n) - Result list: Depends on the number of solutions, worst
O(n^2 * k), wherekis number of solutions.
- Board:
